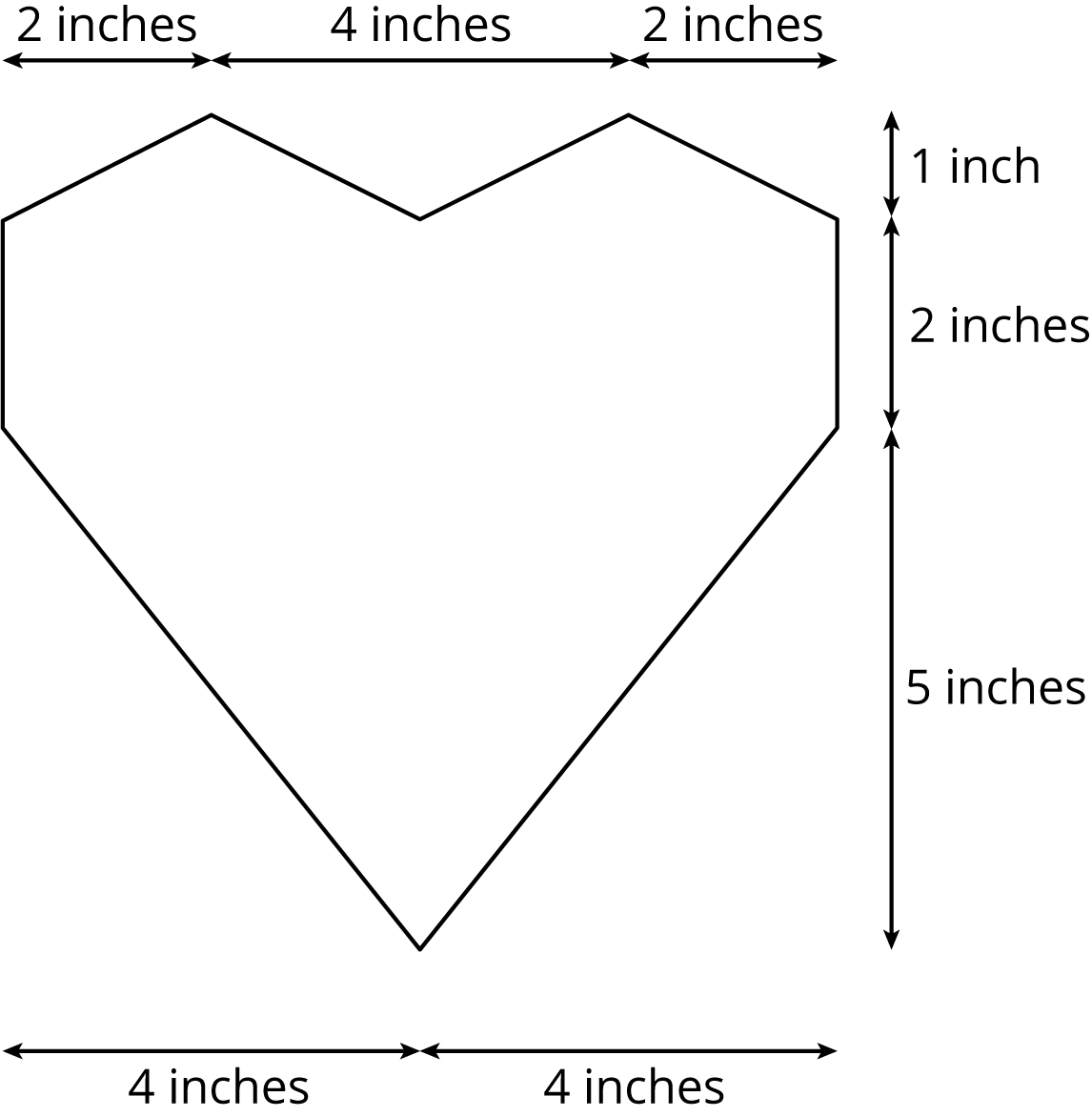
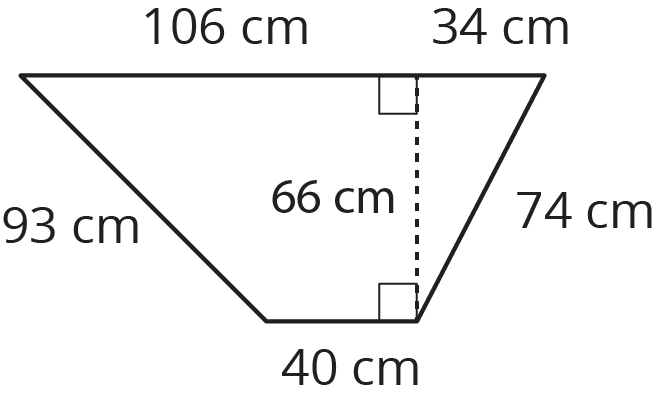
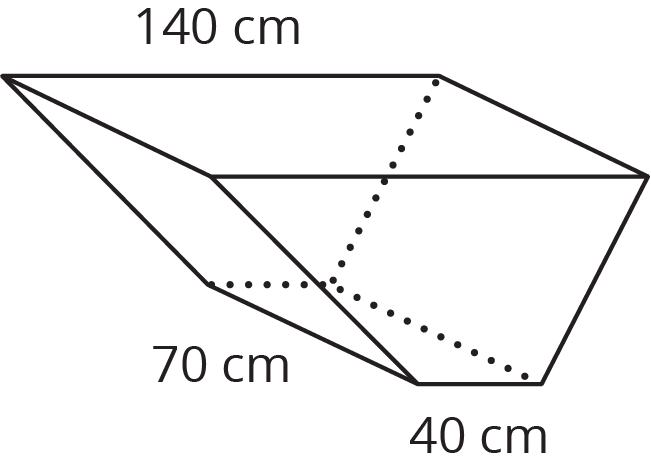
15.1: The Science Fair
Mai’s science teacher told her that when there is more ice touching the water in a glass, the ice melts faster. She wants to test this statement so she designs her science fair project to determine if crushed ice or ice cubes will melt faster in a drink.
She begins with two cups of warm water. In one cup, she puts a cube of ice. In a second cup, she puts crushed ice with the same volume as the cube. What is your hypothesis? Will the ice cube or crushed ice melt faster, or will they melt at the same rate? Explain your reasoning.